The site's hierarchy
Navigation
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 1 |
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 | 31 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
- Les premiers zoom de galaxies sont accessibles
- Le halo FOF 6133 de la boite Horizon L et le halo FOF 544 de Horizon S ont été resimulés avec plusieurs techniques de zoom. Il est important que chaque "zoomer" valide sa méthode, avant de lancer une campagne de zoom sur un plus grand cataloque.
- Les données de la simulation Mare Nostrum sont disponibles
- 34 snapshots jusqu’à z=4 sont accessibles sur horizon3 et sur le serveur de fichiers de l’IDRIS à la collaboration Horizon.
- Méso Machine HPC1 opérationnelle
- Depuis le 23 Octobre 2005, la Méso machine du site horizon est operationnelle. Elle correspond à 3 quadriprocesseurs avec chacun 64 Giga de RAM reliés par infiniband, ainsi qu’un access conséquent (sur une base de projet dédié) au reste de la ferme). Son acces est ouvert a toute personne de la collaboration ayant acces à la minigrille et qui en fait la demande a admin-minigrille
- http://
- Workshop Horizon le 14 et 15 novembre 2005
- Il aura lieu à Paris les 14 et 15 novembre 2005 (prévoir une nuit sur place). L’enregistrement est ouvert dans la rubrique "meeting!"
- http://
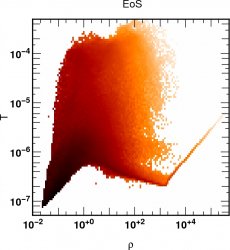
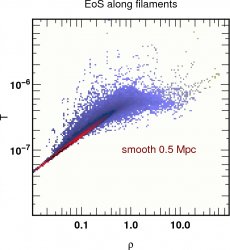
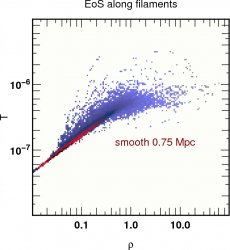
![]() 12th most massive halo Equation of state
12th most massive halo Equation of state  z=4
in code units for the temperature
z=4
in code units for the temperature
The catalogs
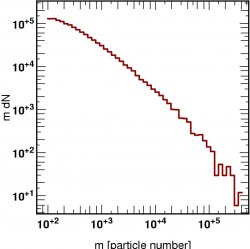
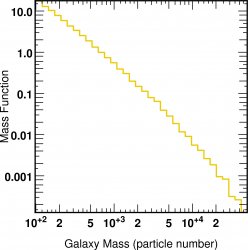
![]() Mass function of Dark Halos (using the above catalog)
Mass function of Dark Halos (using the above catalog)
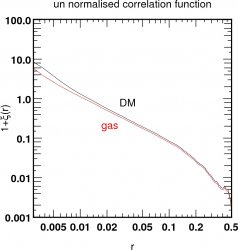
![]() Correlation function (using the cube below)
Correlation function (using the cube below)
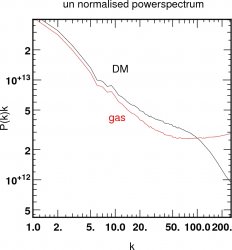
![]() Power spectrum (using the cube below)
Power spectrum (using the cube below)


It can also be viewed interactively as
a 3D java applet at the following
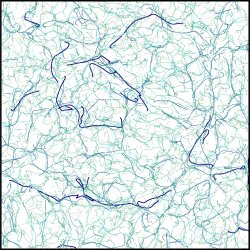
![]() 3D-skeleton-low-res (at low resolution)
and
3D-skeleton-low-res (at low resolution)
and
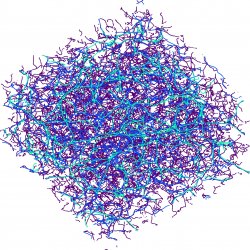
![]() 3D-skeleton-hi-res
(at higher resolution).
3D-skeleton-hi-res
(at higher resolution).
![]() Comparison of all skeletons
Comparison of all skeletons  z=4
z=4
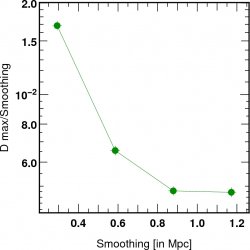
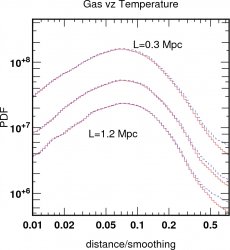
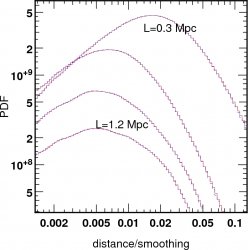
![]() Distance PDF between gas and DM filaments
in units of smoothing.
Distance PDF between gas and DM filaments
in units of smoothing.
The physical size of gas filaments appears here
 R< 800 kpc.
(ie the disance is not scale invariant anymore)
R< 800 kpc.
(ie the disance is not scale invariant anymore)
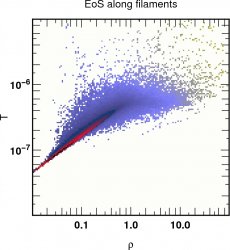
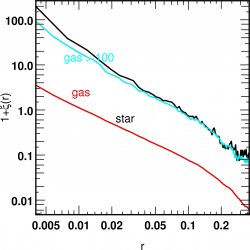
for the dark matter
the beheaviour is not scale invariant: at about 800 kpc the filaments of DM and Gas differ
|
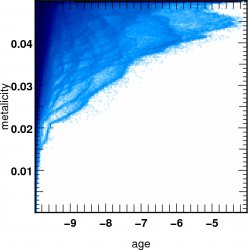
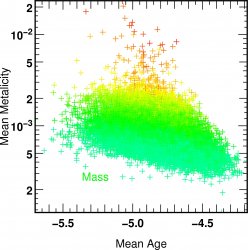
![]() Stars age metallicity relation
Stars age metallicity relation  z=4
z=4
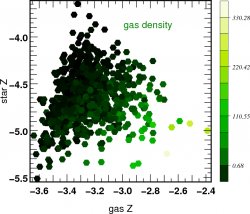
![]() Correlation function of stars and biased gaz
Correlation function of stars and biased gaz  z=4
z=4
![]()
![]() Slices of gas velocity in z
Slices of gas velocity in z  z=4
z=4
The galaxies are identified via a FOF on the stars
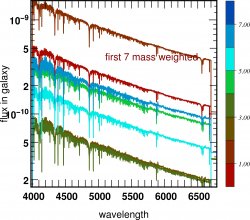
![]() Spectra of galaxies
Spectra of galaxies
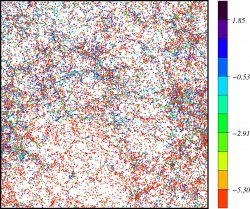
![]() FOF of galaxies
FOF of galaxies
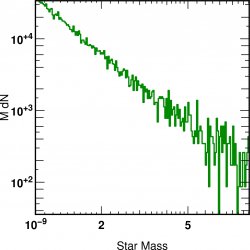
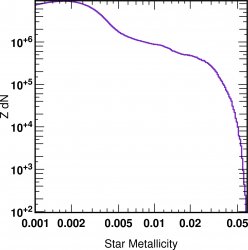
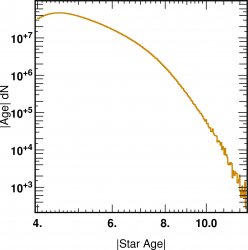
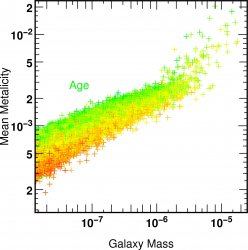
![]() Metallcity age Mass r relations of galaxies
Metallcity age Mass r relations of galaxies  z=4
z=4
a FOF cut of 100 was applied on star selection to construct the galaxies.
The metalicity and the age are mass weighted
|
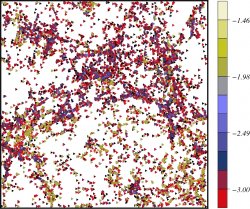
![]() Catalog
Catalog
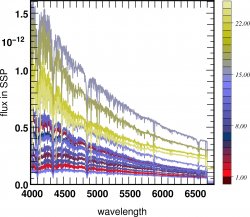
![]() Stellar spectra of galaxies
Stellar spectra of galaxies 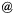 z=4
z=4