The site's hierarchy
Navigation
Mar 2009
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 1 |
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 | 31 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
- CINES received a 150 TFlops machine
- GENCI has acquired for the French University Supercomputing Center a 12288 core SGI Altix. It is ranked 14th in the World and first in France.
- Site Web du CINES
- IDRIS received a 140 Tflops BlueGene/P machine.
- The CNRS supercomputing centre has acquired a new BlueGene machine with 40480 processors and 20 To of RAM memory.
- See the press release.
- Mare Nostrum simulation down to z=1.55
- We carried out our fourth run of MareNostrum down to z=1.55 while producing 150 Million "stars". More info is given here
- Horizon 4Pi 4096^3 down to z=0
- We have carried a full sky 2Gpc/h 4096^3 Dark Matter simulation down to z=0. More details can be found here
- Horizon 4Pi run 2048^3 completed
- We have completed a full sky cone run of DM with RAMSES on platine CEA with 2048^3 particles. See a slice here
- Mare Nostrum @ z=1.9
- We carried out our third run of MareNostrum down to z=1.9 while producing 120 Million "stars"
- Mare Nostrum simulation down to z=2.4
- We carried our second run on the Mare Nostrum supercomputing center down to z=2.4, thanks to 4-fold improvement in overall performance.
- 1024^3 500 h-1Mpc simulation completed
- RAMSES run of the HORIZON initial condition was carried down to z=0 using 1024^3 dark matter particles in a (500 Mpc/h)^3 box with up to 16 levels of refinement (corresponding to local effective resolution of 65536).
- Horizon 1024^3 100 Mpc/h simulation completed.
- A RAMSES run of the HORIZON initial condition was carried down to z=0 using 1024^3 dark matter particles in a (100 Mpc/h)^3 box with up to 16 levels of refinement (corresponding to local effective resolution of 65536).
- A 43 Tflops supercomputer at CEA
- CCRT, the supercomputing centre of CEA, has just received a new BULL supercomputer with 6800 processors and 13.6 Tb of RAM memory. This facility is dedicated to academic and industrial research.
- Lire le communiqué
- MareNostrum simulation published in HPCWire
- Lire l’article
- Fourth Horizon Workshop 2006b
- The 4th workshop takes place from December, the 11th to December, the 12th at Paris Observatory. Registration form available here.
- MareNostrum simulation has started at BSC
- After 1 week of operations, we have reached redshift 4. The simulation will proceed further more during the next quarters. We have started to post-process these initial data.
- Horizon Grid
- The Horizon grid is now in operation. It links the 6 quadri opteron of Meudon, Paris, Lyon, Saclay, IAP and Marseille and is open to all members of the collaboration. Voir ce lien
- http://grille.projet-horizon.fr
- Third Horizon Workshop 2006a
- Horizon Workshop 2006a 10, 11 and 12 april 2006 in Lyon. It will be dedicated to progress reports. Registration form
- Horizon is part of the DEISA "Extreme Computing Initiative"
- Horizon will launch one extreme application for galaxy formation using the DEISA infrastructure at Mare Nostrum http://www.bsc.es
- DEISA web site
- Second Horizon Workshop
- Horizon Workshop 2005 took place at Paris Observatory the 14th and 15th november. It was dedicated to internal discussions and management issues.
- October 2005: Horizon was awarded a 500 k€ grant by ANR, the French Science Foundation.
- Horizon response to «ANR Blanche» Call for Proposals has been succesfull in the «UNIVERS» program.
- ANR web site
- July 2005: HP France was selected to host the Horizon "meso-computer"
- HP company has succesfully answered the "call for proposals" issued by the Hrizon Project for a medium-size dedicated super-computer. The computer will be hosted at HPC1, the HP high performance computing center near Paris.
- February 2005: INSU and CEA agree to fund the Horizon "meso-machine".
- Horizon has submitted to INSU a proposal for funding a medium-size computer dedicated to the project. The proposal was accepted as a joint CEA and INSU operation.
- September 2004: Kick-off meeting in Paris
- During 3 days (13, 14 and 15 of september), 30 scientists have met at Observatoire de Paris to set up the basic organisation and objectives of the Horizon Project.
- KO Meeting
- April 2004: Horizon received official support from ASSNA.
- The french initiative «Action Spécifique pour les Simulations Numériques en Astrophysique» have given to the Horizon project its "label" for outstanding and structuring computational project.
- April 2004: The french Astroparticule program provides financial support for the Horizon "mini-grid"
- The Programme Astro-Particule, a joint IN2P3 and INSU initiative, has agreed to finance 6 quad AMD64 servers dedicated to the Horizon Project.
- January 2004: Review by PNC and PNG
- Both PNG and PNC scientific comitees are officially supporting the Horizon Project initiative.
- Theoretical Virtual Observatory workshop (IAP April 5-6, 2006)
A workshop dedicated to the Theoretical Virtual Observatory will take place at IAP on April 5-6th.
The goal is to bring together experts of the Virtual Observatory and theoreticians who would like to make results of their simulations (e.g. databases or catalogs) or numerical codes available to the worldwild astronomical community.
- Program and speakers
Images
by Teyssier Romain
(Tuesday 13 November 2007)
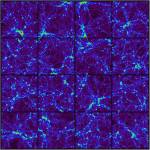 mosaic of 4x4 50 h^-1Mpc simulations (JPG file, 713.6 kb, 1368 x 1368 pixels) Credit C. Pichon, D. Aubert. Each simulation involves 256^3 dark matter particles at z=0. These simulations are produced to study the statistical properties of substructures within dark matter haloes
|
|
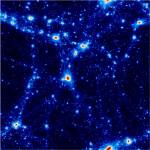 25 h^-1 Mpc slice of dark matter (JPG file, 438.6 kb, 1680 x 1680 pixels) credits D. Aubert, C. Pichon
This high resolution simulation (512^3 particles) is carried as a reference for the purpose of convergence studies. |
|
 50 h^-1 Mpc slice of dark matter (JPG file, 430.8 kb, 1368 x 1368 pixels) credits D. Aubert, C. Pichon This high resolution simulation (512^3 particles) is here represented at redshift 0.5
|
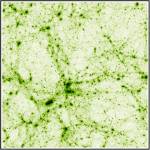
 mosaic of 19x19 50 h^-1Mpc simulations (JPG file, 439.4 kb, 1024 x 1024 pixels) Credit C. Pichon, D. Aubert Each simulation involves 128^3 dark matter particles at z=0. Such sets of simulations are carried to study statistically the properties of dark matter haloes on galactic scales
|
 peack patch of large scale structure (JPG file, 83.4 kb, 964 x 836 pixels) (c) C. Pichon
The flow of trajectories towards their local maxima which define patches of region which will undergo gravitationnal collapse.
|
 Stars in 10 Mpc box (TIFF file, 16 Mb, 4097 x 4097 pixels) Star mass projected along one axis and color-coded according to star age (Yann Rasera)
|
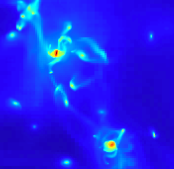 Gas in 10 Mpc box (TIFF file, 16 Mb, 4096 x 4096 pixels) Gas mass projected along one axis color coded according to gas density (Yann Rasera)
|
 A galaxy major merger. (JPG file, 66.8 kb, 1423 x 1423 pixels) Credit Cattaneo, Combes, Colomibi, Bertin, Melchior 2005, Epoch 1, face-on
|
 détection du squelette. (JPG file, 684.8 kb, 1280 x 1024 pixels) Détection des filaments dans une simulation de matière noire de 50 Mpc.
Crédit: Thierry sousbie, CRAL lyon
|
|
 Big initial conditions (JPG file, 1.4 Mb, 2736 x 2736 pixels) This is a slice of a 2048^3 density cube at high redshift, generated by mpgrafic. Credit: C. Pichon, IAP S. Prunet, IAP D. Aubert, CEA |
 Double-ringed galaxy (JPG file, 81 kb, 1365 x 1024 pixels) The galaxy ESO474-G26 (left) and a numerical model of tis formation in a major merger of two spiral galaxies (right). Red and green correspond to the stellar populations of the two progenitor galaxies. Credit : F.Bournaud, F.combes, V.Reshetnikov, LERMA, Paris
|
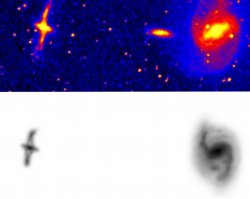 The polar ring galaxy NGC4650A (JPG file, 119.7 kb, 1289 x 1024 pixels) The polar ring (left) is formed via tidal accretion of material from the gas-rich spiral (right, now isolated). The model (bottom) matches the relative velocities of the actual system (top, DSS image) and predicts and age of 400 Myr. Credit F. Bournaud, LERMA, Paris.
|
 Compared evolution of a galactic disk in Newtonian and MONDian gravity (JPG file, 1.1 Mb, 2792 x 1320 pixels) Credit Olivier Tiret, LERMA, Paris.
|
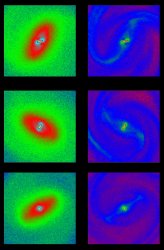 Embedded galactic bars (JPG file, 344.2 kb, 1020 x 1560 pixels) Stars and gas in a gas rich galaxy. A decoupled nuclear bar is seen inside the ILR of the main bar.
Credit: F. Bournaud, LERMA
|
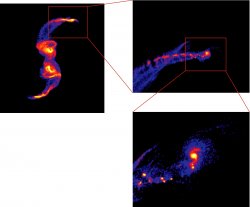 Formation of a massive Tidal Dwarf Galaxy (JPG file, 176.3 kb, 1200 x 993 pixels) This simulation of a merging pair of galaxies, whith several levels of zoom, shows the formation of small clumps and a more massive object at the tip of the tidal tail. This object progressively grows and becomes a massive (>10^9 Mo) tidal dwarf galaxy with its own internal spiral strucutre.
Credit F. Bournaud, LERMA, Paris
|
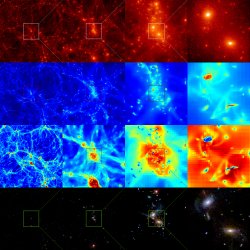 Hierarchical gas dynamics (JPG file, 2.4 Mb, 2048 x 2048 pixels) Two galaxies in the cosmological context: Zooming sequence showing dark matter density, gas density, gas temperature and, star age and distribution. Simulation: 5123 coarse cells/ 5 refinement levels/ box length 10 Mpc / z=3 Credits Y. Rasera, R. Teyssier |
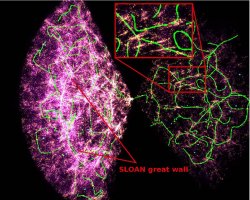 The skeleton of the SDSS (JPG file, 234.4 kb, 966 x 772 pixels) Credits: T. Sousbie,
H. Courtois, C. Pichon, S. Colombi &
the SDSS collaboration
|
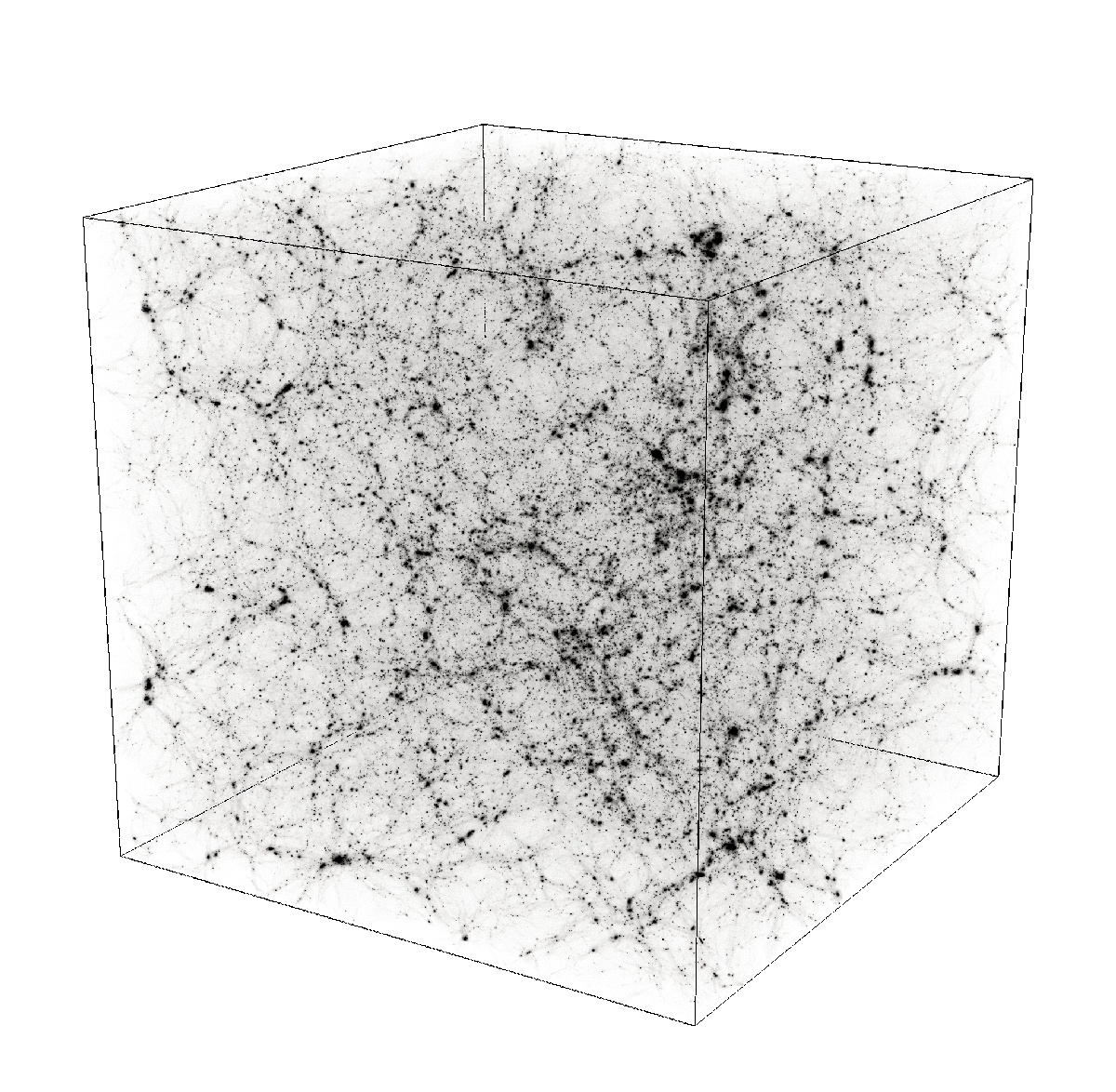
 500 h-1 Mpc oblique slice (JPG file, 4.5 Mb, 4096 x 4096 pixels) 1024^3 dark matter particles (c) C Pichon. R Teyssier 2007
|
|
 50 h-1 Mpc Dark Matter (JPG file, 939.8 kb, 1300 x 1300 pixels) 1024^3 AMR simulation
(c) Sousbie Pichon Teyssier 2007
|
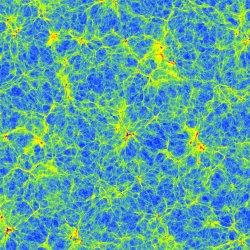 50 h-2 Mpc temperature (JPG file, 3.8 Mb, 2048 x 2048 pixels) oblique slice at z=2.4
(c) Pichon. Sousbie Teyssier 2007
|
 Dark Matter 100^2 h-1 Mpc x 10 Mpc (JPG file, 1 Mb, 1025 x 1025 pixels) slice at z=0
(c) Pichon. Teyssier 2007
|
 Dark Matter 500^2 h-1 Mpc x 50 Mpc (JPG file, 1.2 Mb, 1025 x 1025 pixels) slice at z=0
(c) Pichon. Teyssier 2007
|
 50 h-2 Mpc gas density (JPG file, 3.3 Mb, 2048 x 2048 pixels) oblique slice at z=2.4
(c) Pichon. Sousbie Teyssier 2007
|
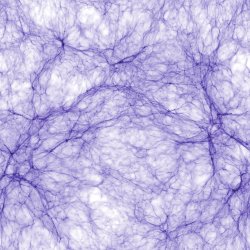 50 h-1 gas  z=2.5 z=2.5(JPG file, 3 Mb, 2048 x 2048 pixels) 1024^3 initial grid; 4 levels of refinements
(c) 2007 Pichon Teyssier
|
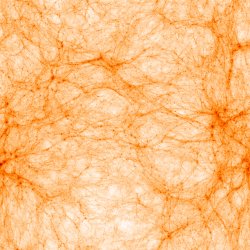
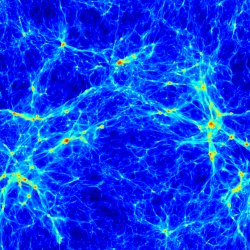 50 h-1 temperature  z=2.4 z=2.4(JPG file, 4 Mb, 2048 x 2048 pixels) 1024^3 initial grid; 4 levels of refinements
(c) 2007 Pichon Teyssier
|
|
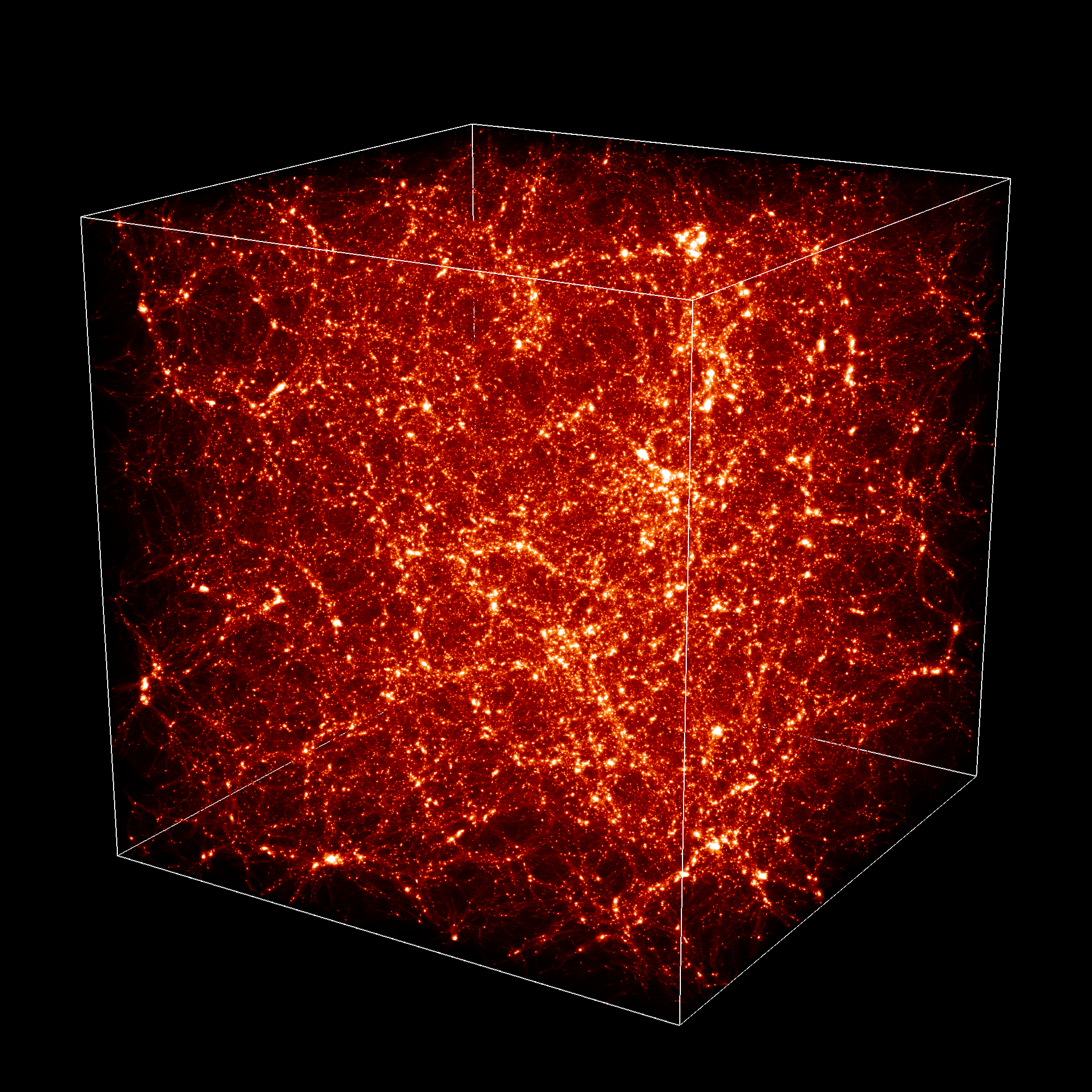
 50h-1Mpc temperature  z=1.9 z=1.9(JPG file, 3.4 Mb, 2048 x 2048 pixels) projection of full box.
(c) C. Pichon R. Teyssier.
|
 50h-1Mpc gas 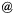 z=1.9 z=1.9(JPG file, 3.3 Mb, 2048 x 2048 pixels) projection of full box.
(c) C. Pichon R. Teyssier.
|
 Horizon 4Pi 4096^3 z=1. (PNG file, 4.5 Mb, 4096 x 2560 pixels) This is a thin slice through a full sky cone.
|
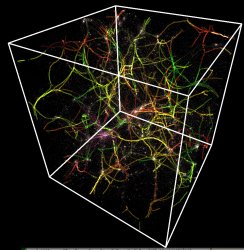 The global skeleton (JPG file, 1.1 Mb, 961 x 986 pixels) superposed onto the dark matter distribution (one particle in a thousant) . (c) Sousbie, Pichon Colombi.
|
 Mare Nostrum galaxies at z=2.4 (JPG file, 1.6 Mb, 2048 x 2048 pixels) Composite image of galaxies in true coiour
|